Neptune: Everything You Need to Know!
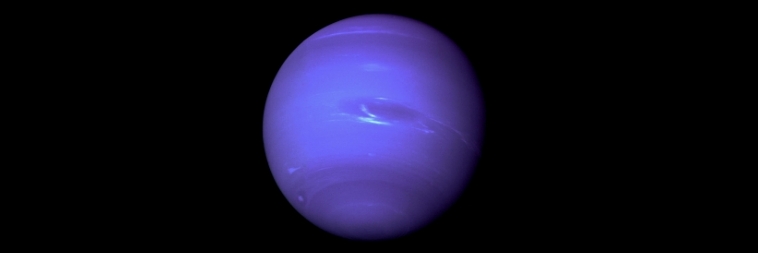
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at Neptune, our solar system’s most enigmatic and distant planet.
Among the most enigmatic of our solar system’s celestial wonders, Neptune stands out as a particularly intriguing subject for astronomers. But what makes this distant blue giant so captivating? Let’s embark on a cosmic journey to uncover the secrets of Neptune!
Key Features of Neptune
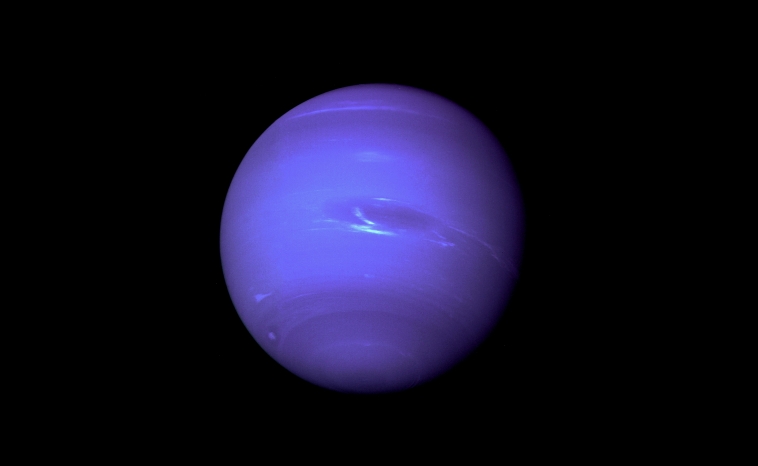
- Location: Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the furthest known planet in our solar system.
- Size: The planet is about 17 times the mass of Earth, making it the fourth largest planet by diameter.
- Distance from the Sun: Positioned approximately 4.5 billion kilometres away, it takes sunlight over four hours to reach Neptune.
- Composition: Neptune primarily comprises hydrogen and helium, like our solar system’s gas giants, Jupiter and Saturn. However, the planet has significantly more water, ammonia, and methane ice, making it known as an ice giant, along with its neighbour, Uranus.
The Discovery of Neptune and Early Observations
In 1612, legendary astronomer Galileo Galilei made plots of the night sky that he had observed through his telescope. These plots included what he believed was a fixed-point star—in reality, this object would turn out to be Neptune!
Interestingly, Neptune was the first planet discovered through mathematical prediction rather than direct observation. In 1846, Urbain Le Verrier calculated the location of a new planet that he believed must be perturbing the orbit of Uranus. Later that year, at the Berlin Observatory, Johann Gottfried Galle would locate Neptune just one degree away from Le Verrier’s predicted location!
Great Dark Spots and Other Phenomena
One of the most famous features of Neptune is the Great Dark Spots. First discovered by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989, these massive storm systems are comparable in size to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. However, while Jupiter’s famous storm lasts for hundreds of years, Neptune’s spots last a few years at a time.
Other fascinating phenomena include high-speed winds that can reach up to 2,100 kilometres per hour and dynamic cloud formations that change rapidly, offering astronomers a visual feast.
Neptune’s Rings
Often overshadowed by Saturn’s magnificent rings, Neptune’s rings are nonetheless captivating and worthy of admiration. Composed mainly of dust particles and some ice, they form faint but intricate structures that encircle the planet. These rings are not as bright or as well-known as Saturn’s, but they certainly hold their own unique charm.
Scientists believe these rings are relatively young, possibly formed by the disintegration of one of Neptune’s moons or by capturing cometary material. Accordingly, studying Neptune’s rings could provide valuable clues about the planet’s formation, its complex gravitational interactions, and its evolutionary history.
The Moons of Neptune
Credit: NASA/JPL, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Original Source: Neptune's Moon Triton Fosters Rare Icy Union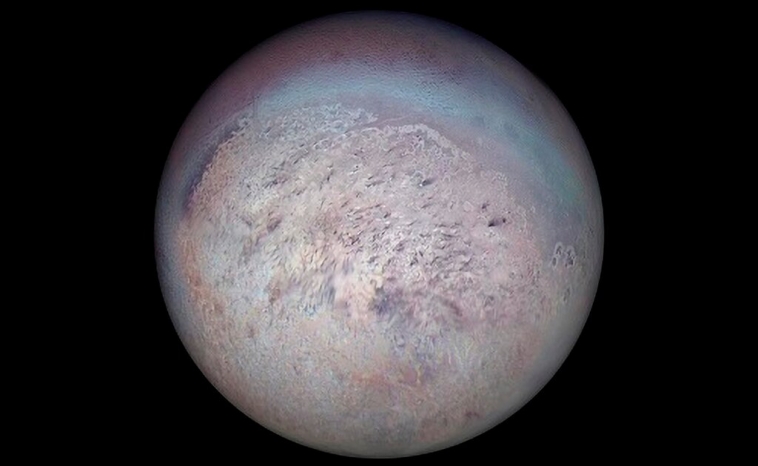
Neptune is home to 16 known moons, but Triton is by far the largest of the planet’s satellites – and the only one that has been rounded by its gravity.
Unlike most moons, Triton orbits Neptune in the opposite direction of its rotation. In fact, it’s the only known large moon with a retrograde orbit in the entire solar system. This could be because Triton was once an independent object captured by Neptune’s gravity. Additionally, Triton has a very thin atmosphere, and its surface is marked by icy volcanoes and geysers that spew nitrogen gas deep into space.
Furthermore, Triton may possess a subsurface ocean that could potentially harbour life. Scientists believe the moon’s interior may be warm due to tidal heating from its eccentric orbit around Neptune.
Exploring Neptune
Only one spacecraft has visited Neptune—Voyager 2 in 1989. However, plans are underway for future missions to explore this mysterious planet and its fascinating moons more closely.
The most recent proposed mission is Trident, which aims to launch in October 2025. This mission would include flybys of Triton and studies of Neptune’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and rings.
Additionally, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope continues to capture stunning images of Neptune and its moons from afar. These images help scientists better understand the dynamics and evolution of this distant world.
Fly Me to the Stars

In our magnificent solar system, Neptune holds a place of unique allure. From its mathematically predicted discovery to its dynamic storms and mysterious moons, this distant giant continues to captivate our imaginations. Whether you’re a seasoned astronomer or a budding stargazer, Neptune offers endless opportunities for exploration and discovery.
Ready to dive deeper into the wonders of our universe? Discover our solar system and beyond with our Fly Me to the Stars VR App. This immersive experience allows you to explore the cosmos like never before, bringing the beauty and excitement of space directly to your fingertips. Download the app today and start your interstellar journey!

