InSight Digging Deep on Mars

What lies beneath the surface of Mars? NASA has sent a rover to dig deep into the Martian surface. Read on to learn more about the special InSight rover.
In May 2018, NASA launched the InSight Mars rover. They expect it to arrive in November 2018. Once it safely lands and sets up for exploration, it will deploy a seismometer. “The mission will study the size, thickness, density and overall structure of the core, mantle, and crust, as well as the rate at which heat escapes from the planet’s interior.” (NASA, 2018) They believe they will learn more about Mar’s evolution. Scientists use seismometers to measure movement in the ground. Things that may make the ground move include volcanic eruptions, earthquakes or explosions.
InSight Tools
InSight is short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport. Along with the seismometer, InSight will carry some other special tools needed to gain information. The Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package instrument will burrow up to 16 feet below the surface to measure the heat coming from Mars’ core. This information will help them determine what the source of the heat is, and whether it shares similarities to our Earth and moon.
The InSight Seismometer sits on the surface of the planet and measures the vibrations of the planet. Furthermore, it will measure wind, pressure, temperature, and magnetic fields to help keep the readings accurate. Dust storms can generate seismic readings as well. “As it reveals what lies beneath, the seismometer may even be able to tell us if there’s liquid water or plumes of active volcanoes underneath the Martian surface.” (NASA, 2017)
InSight carries a particular antenna to measure location information. For example, the rover can determine how much of Mars’ North Pole wobbles as it orbits the sun. The Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment, RISE, will provide detailed information on the size of Mars’ iron-rich core. Together with the other information collected they can find out if the cored is liquid. They may also learn what other elements exist beside iron.
NASA/JPL-Caltech, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons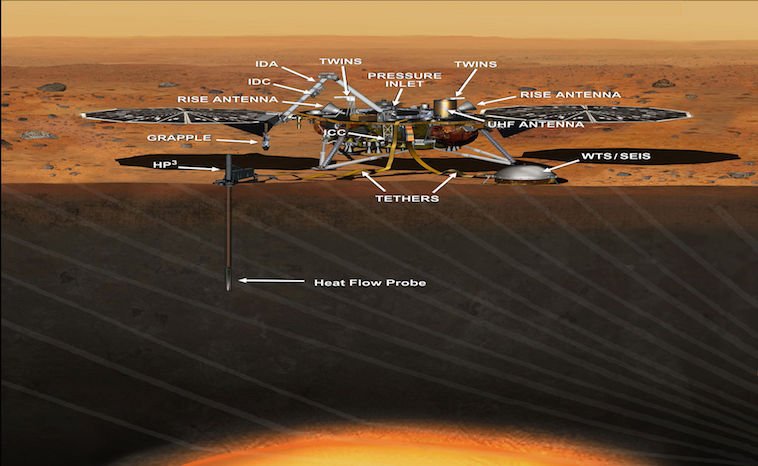
InSight Laser Locator and Cameras
In addition to the main tools, InSight has a temperature and wind monitor, an instrument deployment arm, and an instrument context camera. A special Laster RetroReflector will make precise measurements of the lander’s location. The national space agency of Italy provided the LaRRI. Each of the eight reflectors uses three mutually perpendicular mirrors. These mirrors join at one point in the inner corner of a box. Consequently, it returns incoming light towards its source. Forty- five years ago, Apollo astronauts placed larger corner cube reflectors at several sites on the moon.
InSight has a color camera stationed on the instrument deployment arm. The camera will provide 3d imaging of the surrounding terrain. The wide angle lenses give scientists a 120-degree panoramic view of the rover and its instrument panel.
When InSight lands in November of 2018, it will be 370 miles from rover Curiosity. The location is called Elysium Planitia near the Mars equator. It if lands successfully, InSight will begin a two-year mission collecting data.
We look forward to following the mission and learning more about Mars, its origins and any new insight into its composition. With new knowledge will come the possibility of one day visiting the planet.
