The Colors of Space
 Wallpaper by farrocum on Wallpapers.com
Wallpaper by farrocum on Wallpapers.com
How many colors can the human eye see? Can we see color in space? Read on to learn more about color in space.
Believe it or not the human eye can see about 7,00,000,000 colors. But, did you know that colors exist that you cannot see? Color does not change in space, because the wavelengths remain the same. Although you can see all the colors of the rainbow, plus every color mixture from those colors, you only have three color detectors in your eyes. These color detectors, called cones, have a preference for a particular type of light.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Each cone of your eye reads different parts of the light spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum refers to the entire range and scope of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation and their respective, associated photon wavelengths. Your eyes get excited by the wavelengths and can see the wavelengths for visible light. If you could see infrared, you would see red. If you saw ultraviolet wavelengths you would see violet wavelengths.
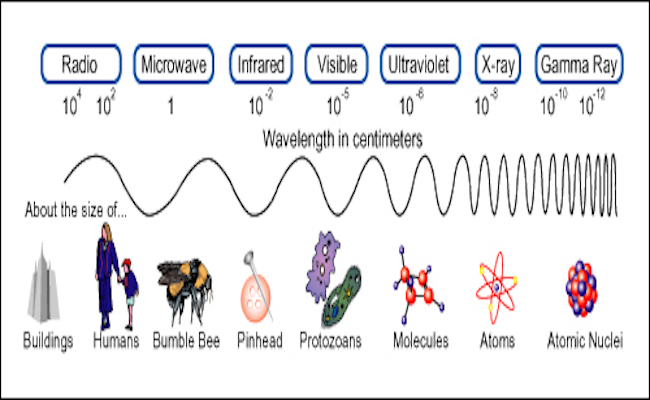
The Visible light (and near-infrared light) is typically absorbed and emitted by electrons in molecules and atoms that move from one energy level to another. This action allows the chemical mechanisms that underlie human vision and plant photosynthesis. The light that excites the human visual system is a very small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. A rainbow shows the optical (visible) part of the electromagnetic spectrum; infrared (if it could be seen) would be located just beyond the red side of the rainbow with ultraviolet appearing just beyond the violet end.
How Your Eyes See
Every object you see reflects light into your eye. That reflected light reaches our small, medium, and large cone cells located in the eye. Each cell reads a wavelength. The cones send a message to your brain telling it how much long, medium, and short wavelength light bounces off an object. Putting all that into a number code we refer to as color. Although light does not have a color, our brain generates a code when the spectrum of light enters the eye.
Color in Space
During the 1990s NASA launched one of the most complex space telescopes into Earth’s Low Orbit. Low Orbit is the altitude between the Earth’s surface and 2,000 kilometers (1,200 mi). Because it is outside our atmosphere, the telescope can view astronomical objects across a broad swath of the electromagnetic spectrum, from ultraviolet light, to visible, to near-infrared wavelengths. The telescope can also see faint objects near bright objects.
The telescope can resolve astronomical objects with an angular size of 0.05 arc seconds, which is like seeing a pair of fireflies in Tokyo from your home in Maryland. This razor-sharp vision is 10 to 20 times better than typical resolution with large ground-based telescopes.
It has revealed a whole new level of detail and complexity in a variety of celestial phenomena, from nearby stars to galaxies near the limits of the observable universe
Why Are Space Imaged Colored?
When we look at a picture of a Nebula taken with the Hubble telescope we see terrific colors emitting from it. But is that how it really appears in space? No, for the sake of science, scientists color the pictures. NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons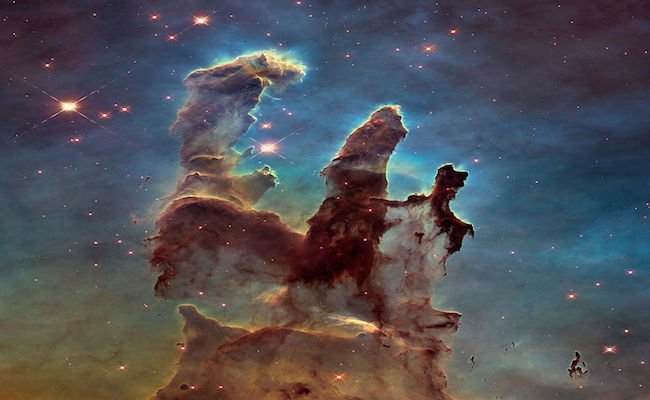
This famous picture of the Eagle Nebula, named Pillars of Creation, shows fantastic colors surrounding the nebula. Researchers will often add artificial colors to focus on an element or feature they are trying to study. Assigning colors to different wavelengths allows them to learn more about each object. Infrared, microwaves, and radio waves give off deep reds. Ultraviolet, X-Rays, and Gamma-rays give of deep violet colors. While the Hubble telescope can detect wavelengths our eyes cannot see, scientists also color them to keep us interested in space.
Several books have been published with colored images of Hubble’s discoveries. You may check also check out this site with up to date pictures of images from the Hubble telescope. Although our eyes cannot see all the colors in the electromagnetic spectrum, we can enjoy the colors of space. Aside from appreciating the beauty of things here on Earth, we can also now enjoy the amazing wonders of space in full color.
