What Is Earth’s Atmosphere Made Of?

Hanging beyond the reach of our tallest skyscrapers and loftiest mountains, our planet’s atmosphere is the envy of all other planets in our solar system. Without it, life would be impossible, and things would look very different on this rock we call home. But what exactly is Earth’s atmosphere made of, and why does it matter?
Our atmosphere does everything, from dictating our weather and climate to impacting communication waves. In this article, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about our gassy life-giver, including examining the composition of Earth’s atmosphere, dissecting its layers, and exploring humanity’s impact on it.
What Is Earth’s Atmosphere?
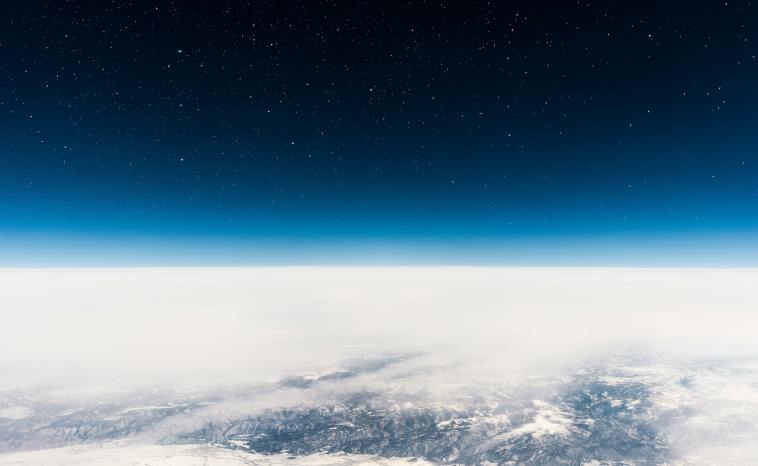

The Earth’s atmosphere is an essential layer of gases enveloping our planet, playing a critical role in sustaining life and influencing our planet’s climate. It serves as a protective blanket, shielding us from harmful solar radiation, keeping our planet warm, and providing the oxygen we need to breathe. Indeed, without it, Earth would be uninhabitable, much like the barren landscapes of the Moon or Mars.
The atmosphere comprises multiple layers, each with unique characteristics and purposes. These layers are primarily defined by the different gases they contain, which also play a significant role in maintaining the balance that keeps Earth habitable.
What Is Earth’s Atmosphere Made Of?
The Earth’s atmosphere is mainly composed of nitrogen (N2), accounting for approximately 78% of its volume. This abundance of nitrogen is vital for supporting life, as it is a fundamental component of amino acids and proteins – the essential building blocks of living organisms.
Following nitrogen, oxygen (O2) is the second most prevalent gas, comprising about 21% of the atmosphere. Oxygen plays a critical role in sustaining life by facilitating respiration, essential for generating energy in most organisms.
The remaining 1% is made up of various other gases, such as argon (Ar), carbon dioxide (CO2), neon (Ne), helium (He), and methane (CH4). Additionally, trace amounts of water vapour (H2O) can be found within the atmosphere, further contributing to its chemical composition.
The intricate combination of these gases creates a dynamic and balanced atmosphere, supporting the diverse ecosystems and life forms that thrive on our planet.
What Are the Layers of Earth’s Atmosphere?
The Earth’s atmosphere features five main layers, each with a distinct composition and temperature profile:
- Troposphere: The lowest layer of the atmosphere, where most weather events occur. It extends up to approximately ten kilometres from the Earth’s surface and contains most of the water vapour in the atmosphere.
- Stratosphere: Located above the troposphere, this layer is characterised by a steady increase in temperature with altitude due to the presence of ozone (O3). This gas absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
- Mesosphere: The mesosphere is the third layer of the atmosphere, extending up to altitudes of about 85 kilometres. In this layer, temperatures decrease with altitude, reaching as low as -100°C near its upper boundary. Additionally, the mesosphere has very low moisture levels and is home to some fascinating phenomena, including airglow and noctilucent clouds.
- Thermosphere: As we move higher into the atmosphere, temperatures rise again, reaching 2000°C in the thermosphere. Curiously, you would still feel pretty cold if you visited the thermosphere because there aren’t enough gas molecules to transfer heat to your body. This layer absorbs most of the X-ray and UV radiation the Sun emits and is also where the International Space Station orbits around the Earth.
- Exosphere: The outermost layer of the atmosphere, gradually blending into the vacuum of space. The exosphere features extremely low gas densities and high temperatures caused by intense solar radiation.
Why Is the Atmosphere Important?

The Earth’s atmosphere plays a multifaceted and intricate role in our planet’s ecosystem. It acts as a protective shield, effectively shielding our planet from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation and safeguarding us from its detrimental effects. Moreover, the atmosphere skillfully regulates the planet’s temperature by effectively trapping the sun’s rays, maintaining a delicate balance that supports life.
But the atmosphere doesn’t stop there. It goes beyond its fundamental functions by providing essential oxygen, a life-giving element that enables the survival of a vast range of organisms. Significantly, this abundant supply of oxygen allows countless species to thrive, contributing to the rich biodiversity that enriches our planet’s interconnected web of life.
Furthermore, the diverse layers of the atmosphere contribute to the intricate regulation of weather patterns, ensuring the harmony of our planet’s ecosystem. From the troposphere to the stratosphere, each atmospheric layer plays a crucial role in shaping weather phenomena, such as cloud formation, precipitation, and wind patterns. This intricate dance of atmospheric dynamics affects the weather on a local scale and influences global climate patterns.
How Have Humans Impacted Earth’s Atmosphere?
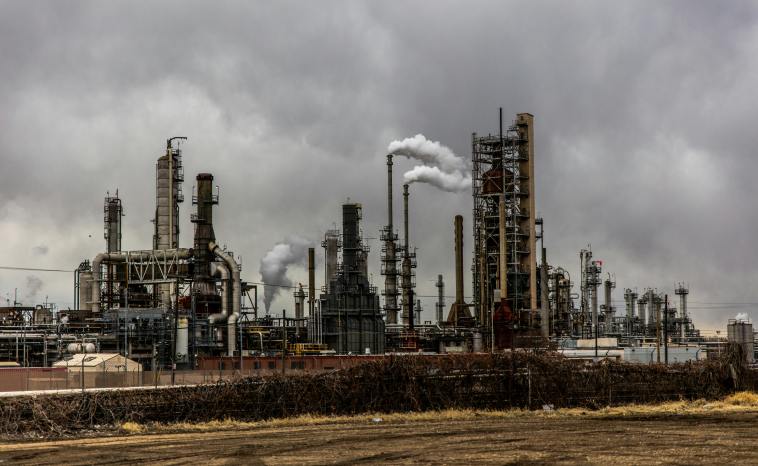

Humanity’s impact on Earth’s atmosphere is quite a conundrum. On one hand, we have witnessed remarkable achievements in engineering, technology, and industry. However, these advancements have come at a significant cost to our planet’s protective shield:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Our industrial activities release copious amounts of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane. Subsequently, these gases thicken the thermal blanket of our atmosphere and lead to global warming.
- Ozone Layer Depletion: Chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), formerly used in refrigeration and aerosol cans, have played havoc with the ozone layer, allowing more UV radiation to reach the Earth’s surface.
- Air Pollution: Fumes and smoke from factories and vehicles are soiling the air we breathe, creating a health hazard and altering the delicate balance of atmospheric components.
All these factors combined have led to climate change, extreme weather events, and an increase in respiratory illnesses.
The OSR Gift Card

Earth’s atmosphere is a complex and vital system. Understanding its composition helps us appreciate the planet we inhabit and underscores the urgent need to protect it.
The future of Earth’s atmosphere depends largely on our actions today. If we continue to emit greenhouse gases at the current rate, we risk altering the delicate balance of our atmosphere, leading to irreversible climate change. Conversely, if we reduce emissions, we can help preserve our atmosphere for future generations.
But astronomy isn’t all worrying about the future – there’s a whole universe of stars, planets, and other fascinating objects we can enjoy right now! With the OSR Gift Card, you can give your loved one the chance to name their own star and leave their mark on the cosmos.

